U.S. Port Disruption and Supply Chain Risks
Forty-seven thousand dockworkers represented by the International Longshoremen’s Association went on strike at midnight on October 1, 2024. The ports they serve stretch from Maine to Houston accounting between 43%-49% of all U.S. imports. A prolonged strike at the ports could lead to major supply-chain disruptions right before the holiday season and potentially have political fallout as the November election nears. J.P. Morgan analysts estimate it would cost the U.S. economy between $3.8 billion and $4.5 billion a day. With this kind of impact, analysts do not expect the strike to last longer than a week, but the ramifications may last much longer.
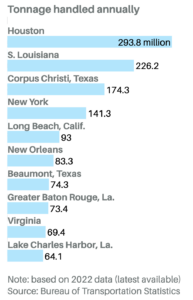
Nine of the 10 most active ports are on the East or Gulf coasts, seven of which are Texas or Louisiana based. However, for this particular strike, according to the API, crude oil imports and exports will not be directly affected, as their workforce is administrated by separate contracts. This strike is more focused on imports of food, vehicles, heavy machinery, construction materials, chemicals, furniture, clothes and toys.
Crude and NGLs: Key Factors to Watch, even if Indirect
While crude oil may not be directly disrupted, the ports of Houston, South Louisiana, and Corpus Christi are heavily tied to the energy sector, meaning indirect effects are inevitable. The energy industry depends on a wide range of secondary markets that rely on global supply chains, including:
- Chemical manufacturing
- Machined parts and equipment
- Vehicles and heavy machinery
- Construction materials
Even without direct port closures for crude, these interdependent sectors could experience higher operating costs. For example:
- Demurrage charges may not increase dramatically, but
- Subsidiary costs such as more expensive machinery or materials will drive up energy prices over time.
Triazine Supply Chain Vulnerability.
Triazine, a chemical essential in natural gas treatment, agriculture, and wastewater management, is highly exposed to global supply chain risks.
- If triazine or its raw materials move through East or Gulf Coast ports, the ongoing strike could cause significant delivery delays and shortages.
- The U.S. both imports and exports triazine. While domestic production is strong, many industries still depend on international supply.
- Major chemical producers like BASF and Dow Inc. play key roles in both production and trade.
- Most domestic manufacturing is concentrated in Texas, making the region particularly sensitive to disruption.
- The Texas freeze in February 2022 demonstrated how unexpected events can cripple supply chains recovery took months. A major port strike could lead to similar long-term instability.
Alternative Solutions and Supply Chain Planning
Alternatives during prolonged outages may find shippers seeking deliveries to West Coast ports; however, diverting shipments may prove to result in even longer delays. If warehouse inventories run out due to a prolonged strike, companies may simply seek non-triazine solutions. For example, when considering treating H2S in crude oil or natural gas, taking into account the product’s supply chain exposure should be studied. Commodity based products such as triazine could be greatly impacted in port strike scenarios.
A prolonged dock worker strike especially along the Gulf Coast ports may not see direct impact to crude and NGL import and exports, but energy prices could ultimately be impacted by the long supply chain effects due to the other impacted industries that are served along these busy ports. A more discrete impact will likely affect Triazine availability, resulting in price volatility due to supply chain bottlenecks and increased transportation costs.
If you’re concerned about your H₂S scavenger supply or need help evaluating alternatives, contact us to speak with our team.
Sources:
https://www.psmarketresearch.com/market-analysis/triazine-market-report







