What is Biogas, and why does it need Treatment?
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), produced when organic materials such as manure break down in anaerobic conditions (without oxygen). However, raw biogas contains impurities like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and water vapor, which make it unsuitable for direct use as a fuel. To convert it into RNG—a clean, pipeline-grade gas—biogas must undergo a treatment process to remove these impurities.
The Biogas Treatment Process
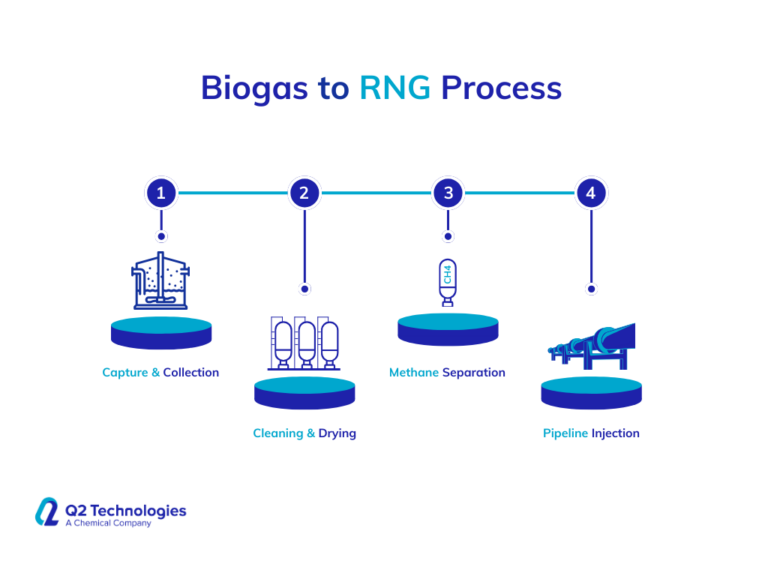
he transformation of biogas into RNG involves the following steps:
- Capture and Collection: Biogas is collected from anaerobic digesters at dairy farms, landfills, or wastewater treatment plants.
- Cleaning and Drying: Impurities such as H2S, CO2, and water vapor are removed through specialized treatment systems.
- Methane Separation: The methane content is concentrated to over 90%, and as one of the least complex hydrocarbon chains, the gas is suitable for direct injection into natural gas pipelines.
- Pipeline Injection: The upgraded RNG is injected into local gas pipelines which is safe and clean for residential to commercial needs such as electricity generation, heating, or as a fuel for vehicles.
What are the Benefits of RNG from Dairy Farms
Environmental Impact
Emission Reduction: Capturing methane from dairy manure prevents it from being released or flared, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Released methane is a greenhouse gas, with 25 times the warming potential of CO2.
Carbon-Negative Energy: RNG replaces conventional natural gas, offering a unique advantage by reducing or even reversing carbon emissions.
Carbon-neutral and carbon-negative energy sources are crucial in combating climate change. By reducing or offsetting emissions, they help stabilize global temperatures and contribute to a healthier planet.
Economic Opportunities
Revenue Generation: Farmers can monetize the biogas they produce by partnering with RNG developers.
Optimized Farm Operations: Collaborating with energy companies allows farmers to improve manure handling processes, maximizing biogas production.
Energy Independence
Domestic Energy Source: RNG reduces reliance on conventional fossil fuels, which are often subject to foreign market fluctuations. RNG supports local economies and promotes energy security.
What is the Market Potential for RNG
The global market for biogas is projected to reach $35 billion in the next five years. Despite this growth, North America’s biogas market remains underutilized. While Europe has over 10,000 biogas production sites, North America has only 2,000. With thousands of dairy farms, landfills, and wastewater treatment plants currently flaring low-quality biogas, there is significant potential to expand RNG production.
Key Statistics
- Dairy farms account for a large portion of livestock emissions, representing a major opportunity for RNG development.
- In the United States, methane emissions come from livestock (31%), landfills (17.7%), and wastewater treatment plants (4%).
- RNG can displace conventional natural gas in industries, homes, and even vehicle fleets across North America.
Developers are working with dairy farms to turn manure into renewable energy. By upgrading the biogas generated by digesters, farmers contribute to reducing emissions while gaining a new source of income. RNG projects also provide healthy returns for investors and project partners, making it a win-win for both the environment and the economy.
What is the Role of RNG in Achieving Carbon-Negative Energy?
Renewable Natural Gas offers a practical and impactful way to curb emissions, generate clean energy, and support local economies. By investing in RNG projects we can transform waste into a valuable resource. This process not only helps meet environmental goals but also provides economic opportunities and energy security. With the North American biogas market poised for growth, now is the time to harness its full potential and drive a sustainable future.
Interested in learning more about how we treat Biogas? Contact us today.






