Hydrogen Sulfide in the Pulp and Paper Industry
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) is a toxic substance that can be found in several industries, including oil and gas, landfill and biogas, wastewater treatment, and pulp and paper. In today’s blog, we’ll focus on the pulp and paper industry, exploring how H2S is a common byproduct of the process and discussing ways to mitigate this noxious gas.
The History and Importance of Papermaking.
Papermaking has been around for quite a while – in fact, it dates back to the first century AD. Further, papermaking has commonly been associated as one of the Great Four Inventions of China, alongside the compass, gunpowder, and printing. Prior to the 1800s, papermaking was very much an artesian process of mold-shaped papers. Since then, however, with more and more automation and consistent quality standards, pulp and paper products have become essential components of various industries. Regardless of individual usage, it is nearly impossible to avoid consuming commercial or domestic paper goods in the modern world.
We’ll dive into the complexities and concerns surrounding H2S in the pulp and paper process in a minute. But first, let’s recognize that today, despite the digital focus we have on modern applications and services, the pulp and paper industry remains one of the largest industries in the world. Unsurprisingly, nations that have a plethora of timber and other pulp sources are leading the way, namely the United States, China, Brazil, and Canada as some of the major players contributing to this globalized product.
Global Leaders in the Pulp and Paper Industry
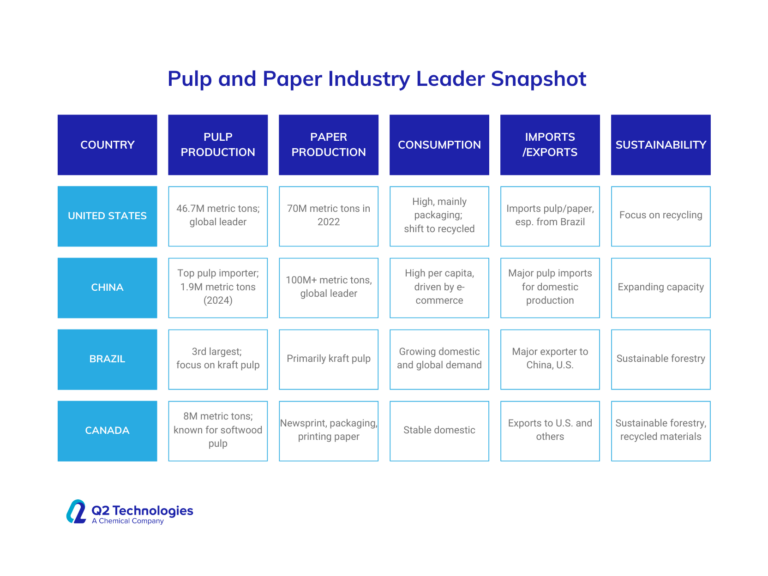
United States
- Pulp Imports: China is the world’s largest importer of wood pulp, with imports surging to over 1.9 million metric tons in 2024. This is driven by its massive paper production capacity and increasing demand for paper-based products.
- Paper Production: China leads globally in paper production, exceeding 100 million metric tons annually, and continues to invest in expanding its production capacity to meet domestic and international demand (UNECE).
- Consumption: China has one of the highest per capita consumption rates of paper products globally, primarily due to the rapid expansion of e-commerce and packaging needs (ResourceWise).
China
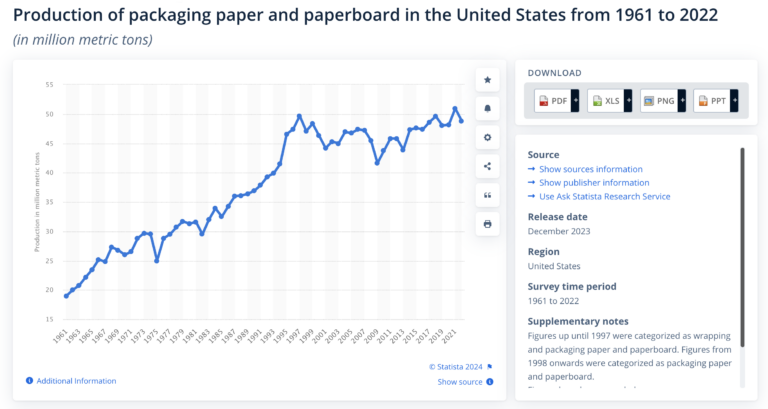
- Pulp Production: The U.S. is one of the largest producers of pulp, generating over 46.7 million metric tons of pulp annually, making it a global leader in pulp production.
- Paper Production and Consumption: The U.S. produced over 70 million metric tons of paper and paperboard in 2022. The consumption of paper products remains high, driven by packaging materials, though there’s been a shift toward sustainable and recycled materials.
- Imports: Despite its large production capacity, the U.S. imports pulp and paper products, particularly from countries like Brazil, to meet its internal demand (ResourceWise) (UNECE).
Brazil
- Pulp Production: Brazil is the third-largest pulp producer, with its focus on market pulp, particularly kraft pulp. It has rapidly expanded production and is expected to increase capacity by 2024. The country is also the top producer of kraft pulp globally.
- Exports: Brazil is a major exporter of pulp, especially to countries like China and the U.S. Its pulp exports are driven by abundant forest resources and sustainable forestry practices (ResourceWise)
Canada
- Pulp and Paper Production: Canada is a significant player in both pulp and paper markets. It produces around 8 million metric tons of pulp annually. Canada is known for its softwood pulp, which is highly valued for making high-strength paper products.
- Exports: Canada exports a significant portion of its pulp, particularly to the U.S., and also exports paper products. The country’s paper production is diversified, including newsprint, packaging, and printing paper (UNECE).
- Sustainability: Canada’s industry is heavily focused on sustainable forestry and the use of recycled materials, contributing to its competitive position in global markets (UNECE).
Pulp and Paper Industry Leader Snapshot
Managing Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Pulp and Paper Processes
Managing H2S Risks
The concerns around H2S in the pulp and paper making process are attributed to several factors, namely the mechanical and chemical process employed to breakdown pulp and the noxious byproducts these processes generate. This is of serious concern for individuals who work around this type of equipment and must stay vigilant to ensure their safety. In the Kraft process, wood chips are cooked in a solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium sulfide (Na2S). During this cooking process, organic sulfur compounds are converted into H2S and other sulfur gases. The release of H2S can occur at several stages of the process, including:
- Digesters: Wood chips are cooked in a vessel with a mixture of chemicals known as white liquor, under high temperature and pressure. This breaks down the lignin and separates the cellulose fibers.
- Pulp Washing: The resulting pulp is washed to remove dissolved lignin and chemicals, off gassing continues to occur.
- Evaporators: The spent cooking liquid, white liquor, is collected and a concentrate forms, known as black liquor.
- Recovery boilers: Black liquor can be burned to recover chemicals and generate en
Handling and mitigating H2S in the pulp and paper industry involves several strategies to ensure safety and compliance with environmental regulations here are a several of the main examples:
- Gas collection: Treatment infrastructure such as scrubber towers is used to capture H2S, which is piped to incinerators that burn it into sulfur dioxide (SO2).
- Chemical processes: Oxidation or alkaline substances are used to treat or neutralize H2S.
- Bioreactors: Biological microorganisms are introduced to convert the H2S into sulfates.
Process optimization is a key consideration throughout this process. Implementing one or several of the above-mentioned practices, among others, including leak detection initiatives, will greatly reduce the amount of H2S generated and lessen the risk of employees being exposed to this deadly gas.
Dealing with H2S effectively does require managing certain costs related to equipment upkeep, chemical spend, and safe operations. However, these costs are balanced by economic drivers: regulatory compliance, which avoids fines and penalties for non-compliance; worker safety, which reduces health risks and associated costs from H2S exposure; and increased productivity, as optimized runtimes help mitigate interruptions due to H2S issues.
To learn more about how Q2 Technologies is transforming the pulp and paper industry’s approach to managing H2S, click here to connect with our team.
Sources:
https://www.statista.com/markets/410/topic/961/pulp-paper/#overview







